Materials
Ceramic Materials
Advanced ceramic materials are produced using highly refined and purified powders that, in many cases, are synthetically produced using high temperatures or chemical reactions. When formed and sintered properly these powders result in product that are very strong, very high in abrasion resistance, can withstand high use temperatures, very good chemical resistance, and very stable.
Advanced ceramics such as alumina, aluminum nitride, zirconia, silicon carbide, silicon nitride and titania-based materials, each with their own specific characteristics, offer a high-performance, economic alternative to conventional materials such as glass, metals and plastics.
Why Ceramic?
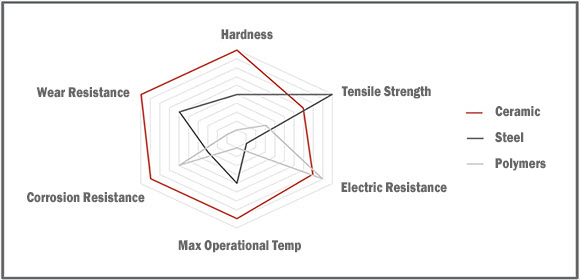
Technical ceramic materials have the ability to make products lighter, more efficient, longer lasting, reduce maintenance intervals, and reduce operating costs.
They are frequently being used to replace metals, polymers, and refractory materials in a wide variety of applications due to their notable high temperature capability, hardness, and electrical properties.
How Choosing Ceramic Material
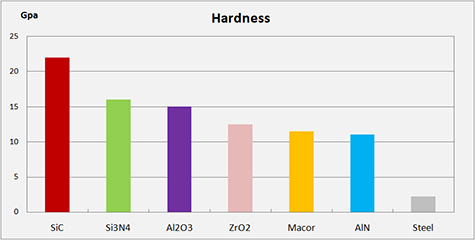 One of the most common properties of engineered ceramics is extreme hardness (& stiffness) – some are more than 4 times harder than stainless steel.
One of the most common properties of engineered ceramics is extreme hardness (& stiffness) – some are more than 4 times harder than stainless steel.
This high hardness directly translates into excellent wear resistance, meaning that many technical ceramics have the ability to keep their precise, high-tolerance finish much longer than any other material.
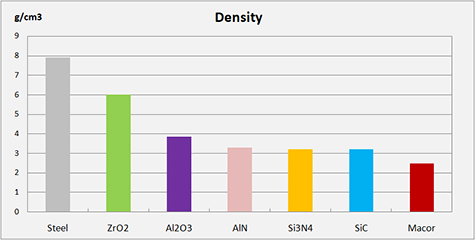 Another common property of technical ceramics is their low density. This is significantly lighter than stainless steel and titanium with only the much softer aluminum being similar in density.
Another common property of technical ceramics is their low density. This is significantly lighter than stainless steel and titanium with only the much softer aluminum being similar in density.
Due to their high hardness and low weight, technical ceramics are increasingly being used in a variety of industries in applications where no other material can match their performance & long life.
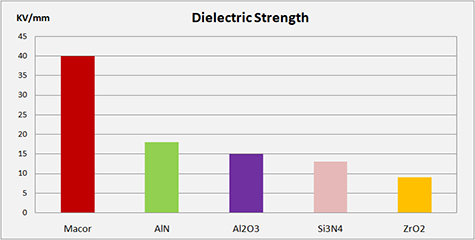 Technical ceramics tend to be excellent electric insulators (high dielectric strength). They are especially useful in high-temperature applications where other materials’ mechanical & thermal properties tend to degrade.
Technical ceramics tend to be excellent electric insulators (high dielectric strength). They are especially useful in high-temperature applications where other materials’ mechanical & thermal properties tend to degrade.
Some ceramics have low electrical loss & high dielectric permittivity; these are typically used in electronic applications like capacitors and resonators.
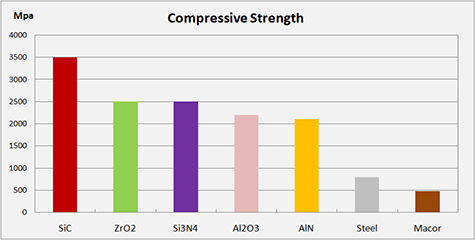 Technical ceramics have very high strength, however, this is only when compressed. For example, many technical ceramics can withstand extremely high loads ranging from 1000 to 4000 MPa.
Technical ceramics have very high strength, however, this is only when compressed. For example, many technical ceramics can withstand extremely high loads ranging from 1000 to 4000 MPa.
Titanium on the other hand, which is regarded as a very strong metal, only has 1000 MPa of compressional strength.
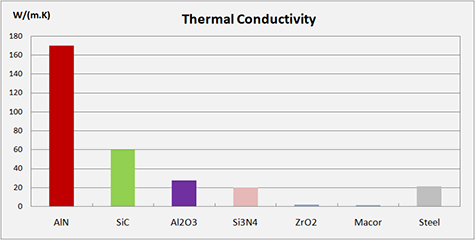 Different types of technical ceramic materials have wildly varying thermal properties. There are some ceramics (Aluminum Nitride) that are highly thermally conductive and are commonly used as heat-sinks or exchangers in many electrical applications.
Different types of technical ceramic materials have wildly varying thermal properties. There are some ceramics (Aluminum Nitride) that are highly thermally conductive and are commonly used as heat-sinks or exchangers in many electrical applications.
Other ceramics are much less thermally conductive, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
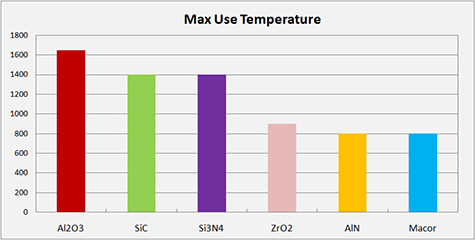 Technical ceramics can function in situations where no metal can maintain their properties. Some ceramics can operate in temperatures in excess of 1750°C, putting them in a class of their own as ultra-high-temperature materials. These ceramics have proven to be invaluable in high-temperature applications like engines, turbines, & bearings where they have increased the lifespan, performance, and efficiency.
Technical ceramics can function in situations where no metal can maintain their properties. Some ceramics can operate in temperatures in excess of 1750°C, putting them in a class of their own as ultra-high-temperature materials. These ceramics have proven to be invaluable in high-temperature applications like engines, turbines, & bearings where they have increased the lifespan, performance, and efficiency.
Material Properties
PROPERTIES | Unit | Alumina | Zirconia | Si3N4 | SiC | Macor | AlN |
Colour | Ivory | White | Black | Black | White | White Grey | |
Density | g/cm3 | 3.8 | 6.0 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 2.7 | 3.4 |
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES | |||||||
Hardness (Vickers 500g) | Gpa | 15.7 | 12.7 | 16 | 26 | 11.5 | 11 |
Modulus of Elasticity | Gpa | 350 | 200 | 300 | 410 | 65 | 320 |
Flexural Strength | MPa | 340 | 1150 | 600 | 500 | 108 | 310 |
Compressive Strength | MPa | 2100 | 2500 | 2500 | 3500 | 480 | 2100 |
Fracture Toughness | MPam 1/2 | 4.0 | 12.0 | 6.0 | 4.0 | 1.5 | 2.6 |
THERMAL PROPERTIES | |||||||
Max. use Temp. | °C | 1500 | 800 | 1400 | 1600 | 800 | 800 |
Thermal Conductivity | W/m.K | 27.5 | 2.5 | 20 | 60 | 1.6 | 170 |
Thermal Expansion Coeff. | 10 -6 /°C | 8.0 | 10.0 | 3.1 | 3.7 | 8.6 | 4.8 |
Thermal Shock Resistance | △T°C | 200 | 250 | 600 | 400 | 200 | 400 |
Specific Heat | J/kg.K | 800 | 500 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 720 |
ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES | |||||||
Dielectric Strength | KV/mm | 15 | 5 | 10 | – | 40 | 18 |
Dielectric Constant | εr | 9.5 | 12 | 6 | – | 7 | 8.8 |
Volume Resistivity | Ωcm | ≥10^14 | ≥10^10 | ≥10^14 | ≥10^15 | ≥10^16 | ≥10^14 |
Dielectric Loss Angle | 1MHz | 0.0004 | 0.001 | – | – | 0.001 | 0.3 |




